The method allows you to identify and characterize materials. DSC Differential Scanning Calorimetry Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is one of the thermalanalysis techniques.

9 Dsc Power Compensation Principle Download Scientific Diagram
This is the part 1 and will be completed in two parts.

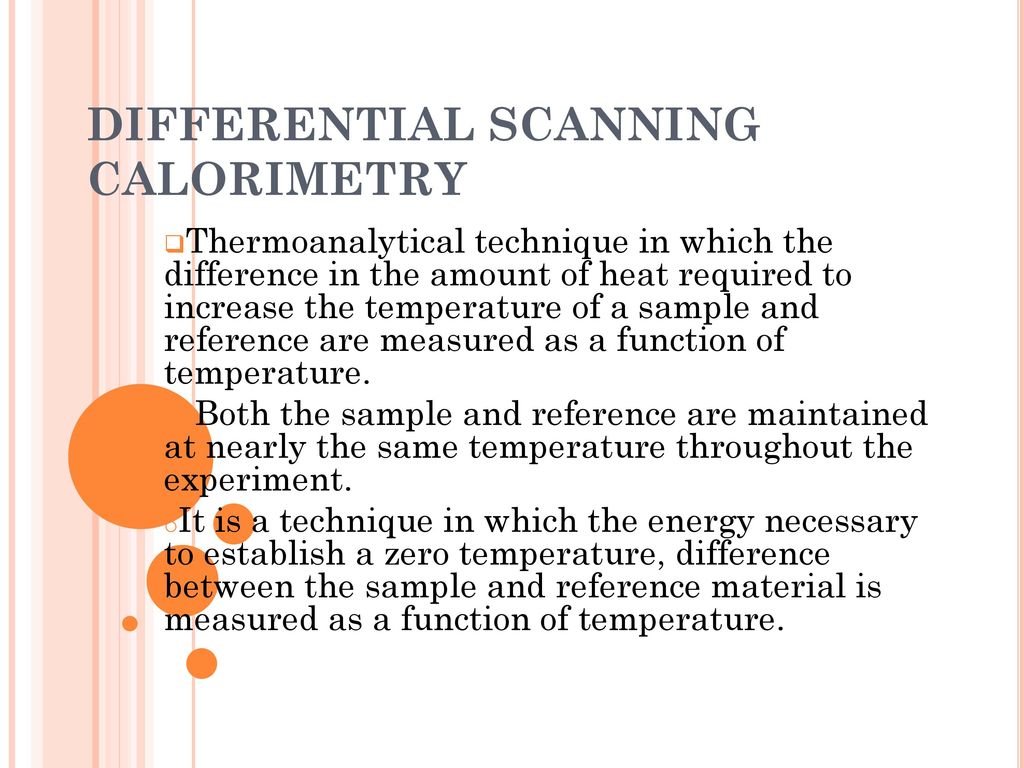
. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a technique for measuring the energy necessary to establish a nearly zero temperature difference between a substance and an inert reference ma- terial as the two specimens are subjected to identical temperature regimes in an environment heated or cooled at a controlled rate. As the principle of DSC is covered in another chapter Analytical Methods. This tutorial describe the differential Scanning Calorimetry in detail.
A differential calorimeter measures the heat of sample relative to a reference. In case of DSC. 422331 Differential scanning calorimetry.
Both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the experiment. The differential scanning calorimetry DSC studies showed an anomalous response whereby at slow heating rates 2C min1 a small exotherm followed immediately by an endotherm was observed. Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSC most popular thermal analysis technique DSC measures endothermic and exothermic transitions as a function of temperature Used to characterize polymers pharmaceuticals foodsbiologicals organic chemicals and inorganics Transitions measured include Tg melting crystallization curing and cure kinetics.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry We must understand that the principle of this calorimeter is actually differential scanning calorimetryDifferential Scanning Calorimetry DSC measures the input material and reference. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is routinely used to determine the glass transition temperature T g for dairy powders. Everyone WELCOMEComplete handmade notes for MSc.
Kanhaiya Patel Hello. Power your next discovery with top quality products and technologies from SigmaAldrich. Principle To maintain the sample and reference at equal temperature during the physical transformations of the sample like phase transitions either more or lesser amount of heat is required to be.
Ad Dedicated to making research and biotech production simpler faster and safer. The basic principle underlying. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is the most frequently used thermal analysis technique alongside TGA TMA and DMA.
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is one of the thermo-analytical techniques. This part discusses in detail. A differential scanning calorimeter does all of the above and heats the sample with a linear temperature ramp 3.
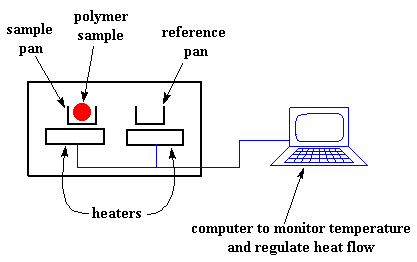
A calorimeter measures the heat into or out of a sample. DSC Differential Scanning Calorimetry is a technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference are measured as a function of temperature. DSC is used to measure enthalpy changes due to changes in the physical and chemical properties of a material as a function of temperature or time.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry this section briefly reviews the recent improvements in DSCs application used in dairy powders. When a sample undergoes a physical transformation such as a phase transition more or less heat will need to flow to it than to the reference typically an empty sample pan to maintain. This article summarizes some information to explain the working principle of the differential scanning calorimeter.
Ad Browse Discover Thousands of Medical Book Titles for Less. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a technique that can be used to determine phase transition temperatures Tg Tm and heat capacities Cp of the analyzed samples. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC measures temperatures and heat flows associated with thermal transitions in a material.
The samples are loaded into a pan of known dimensions hermetically sealed in some cases and heated at a fixed rate C min. Learn about the principles of Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSCDifferential Scanning Calorimetry DSC is a technique for understanding the stability o. Ad Established 22 Years Ago Materials Analysis Testing Quality Control.
Chemistry semester examinationIn These PDFs you will get all topics de. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Principle Instrumentation Application Of Dsc Youtube

Differential Scanning Calorimetry An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Principle Of Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Download Scientific Diagram
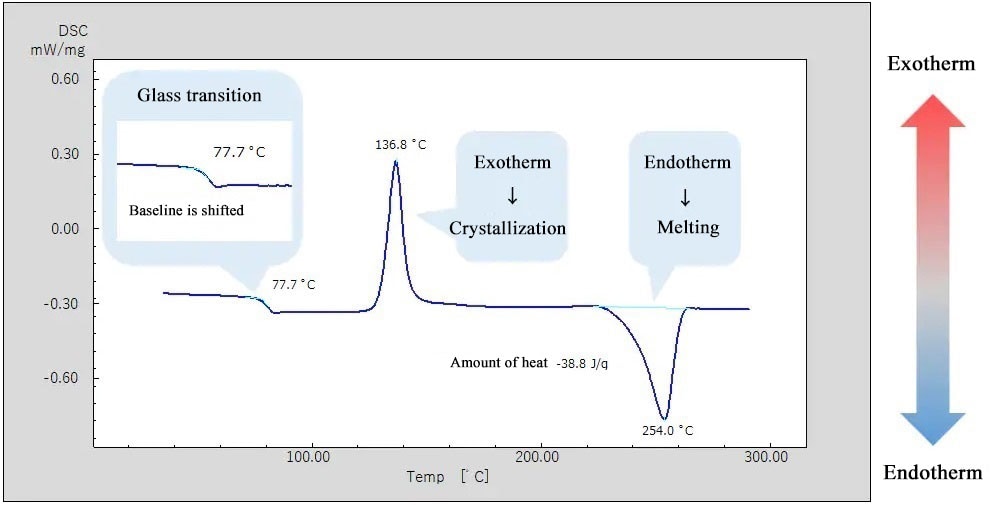
Chapter 2 What Is A Dsc Shimadzu Shimadzu Corporation
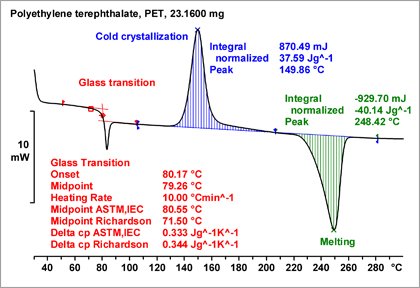
Dsc Analysis Fundamentals And Applications
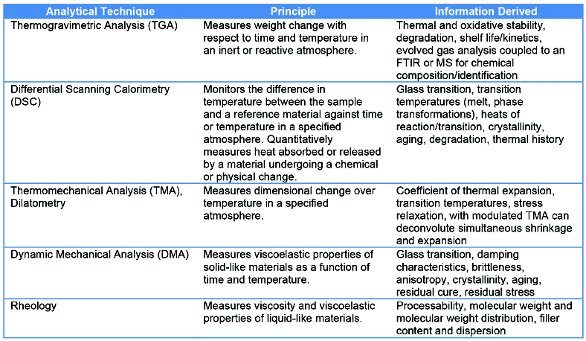
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc As An Analytical Tool In Plastics Failure Analysis American Laboratory
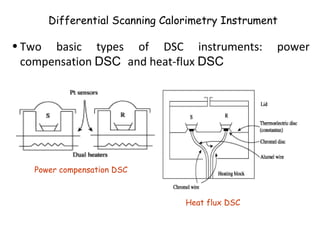
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
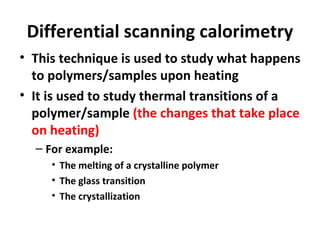
Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Online Training Course Youtube

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Eindhoven University Of Technology Research Portal

Differential Scanning Calorimetry How Does It Work

M6 Differential Scanning Calorimetry Review Of Operating Principles And Applications In Themal Anal Youtube
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Ppt Download
Differential Scanning Calorimetry A Review Open Access Journals

A Setup Of A Heat Flux Differential Scanning Calorimeter B Cross Download Scientific Diagram
Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Solid State Chemistry Aalto Aalto University Wiki

Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Analyses Et Surface Au Coeur De La Matiere
